Social Media
Instagram LinkedIn Pinterest Snapchat TikTok Twitter YouTube
Alphabet Amazon Coca-Cola Costco Ebay Home Depot KFC McDonald’s Mountain Dew Nestle Starbucks Uber Snack Food
Another Detailed SWOT Analysis of Amazon
The SWOT analysis of Amazon is given below:
Strengths
1. Strong brand name – As a global e-commerce giant, Amazon has a strong position and successful brand image in the market.
2. Brand valuation – According to Interbrand’s Global Brand Ranking 2019, Amazon is ranked at #3 position (after Apple at #1 and Google at #2), with a brand value of $125 Billion.
3. Customer oriented – Amazon caters to a large number of customers for everyday needs at inexpensive prices. This has made it a customer-oriented brand.
4. Differentiation and Innovation – Amazon frequently brings creative ideas and innovative additions to its product line and service offerings like ambitious drone delivery service and Withings Aura Smart Sleep System. This creates a differentiation from other companies.
5. Cost Leadership – Amazon doesn’t incur costs in maintaining physical retail stores by selling everything online. With economies of scale, Amazon efficiently controls its costs and lowers its inventory replenishment time. The company has formed numerous strategic alliances with many companies like Evi Technologies, Thalmic Labs, Shoefitr, The Orange Chef etc. It has a strong value chain system which also helps in maintaining a low-cost structure.
6. Largest Merchandise Selection – Amazon owns extensive product mix which attracts online customers to make their majority of purchases from it rather than other online retailers. As of 2018. Amazon has sold 562.3 million products in its Amazon.com Marketplace.
7. Large number of third-party sellers – Due to the high traffic volume on Amazon’s sites, a large number of third-party sellers have joined the platform of Amazon to sell their own merchandises. The data from Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA) reveals that there are more than 2 billion items available from third-party sellers.
8. Go Global and Act Local strategy – This strategy has benefited Amazon the most. Amazon develops partnerships with local supply chain companies that help it in competing against domestic e-commerce rivals. It understands the local needs and launches its services as per the country’s culture.
In India, for example, it has launched a market campaign “Aur Dikhao” to encourage users to search more of its products.
9. Large number of acquisitions – The successful acquisitions of Whole Foods, Zappos.com, woot.com, Junglee.com, IMBD.com, and many others have produced significant revenues and profits for Amazon.
10. Involved into 3 key business – Amazon Marketplace, Amazon Web Services (AWS), and Amazon Prime are 3 key businesses of Amazon which work and support each other. As a whole, they generate massive profits and advantages for the company.
11. Highest revenues in the industry – With over $778.39 billion market capitalization and above $200 billion annual revenues, Amazon is the market leader with the highest revenues in the industry.
12. Superior logistics and distribution systems – Amazon uses highly efficient logistics and distribution systems. It even has fixed rates for different delivery time periods. Thus, it executes reliable, secure, and fast delivery of goods and products to the customers.
Weaknesses
1. Easily imitable business model – Online retail businesses have become quite common in this digital world. So imitating Amazon’s business model for rival firms is not so difficult. A few businesses are even giving Amazon a tough time. These include Barnes & Noble, eBay, Netflix, Hulu, and Oyster etc.
2. Losing Margins in Few Areas – In few areas such as India, Amazon has faced losses. It’s free shipping to customers can be one of the reasons that expose the risks of losing margins in some markets.
3. Product Flops and Failures – Its Fire Phone’s launch in the US was a big failure while its Kindle fire device didn’t even grow well.
4. Tax Avoidance Controversy – Tax avoidance in Japan, UK and US has sparked negative publicity for Amazon. President Trump has recently criticized Amazon over taxes on social media network.
5. Limited brick-and-mortar presence – Amazon owns very limited physical stores. This sometimes hinders to attract customers buy things which are not sellable on online stores.
6. Vox published negative reports related to employees’ treatment and workplace conditions against Amazon in July 2018. Poor air conditioning, timed bathroom breaks, and constant video surveillance are few of the negative remarks made by the employees. Such things affect the market reputation of Amazon.
Opportunities
1. Amazon can gain the opportunity to penetrate or expand its operations in developing markets.
2. By expanding physical stores, Amazon can improve competitiveness against big box retailers and engage customers with the brand.
3. Amazon has the opportunity to improve technological measures and organizational policies to reduce counterfeit sales. One case of counterfeit sales came into light when Amazon sold a fake My Critter Catcher. The product was sold for $1 less than the original product.
4. Can do backward Integration by expanding its production of in-house brands such as Amazon basics to differentiate its offerings and improve profit margins.
5. More acquisitions of e-commerce companies can increase the company’s market share and reduce the competition level.
Threats
1. Few controversies have caused a dent in Amazon’s brand image. People critically reacted and boycotted Amazon sites in 2010 when they found that it’s selling the book “The Pedophile’s Guide to Love & Pleasure: a Child-lover’s Code of Conduct.”
2. Government regulations can also threaten the business proceedings of Amazon in some critical countries. Amazon does not ship to Cuba, Iran, North Korea, Sudan, and Styria.
3. Increasing cybercrime can affect the network security system of the company.
4. Aggressive competition with big retail firms like Walmart and eBay can give Amazon a tough time in the future.
5. Imitation is easy as many new entrants are coming up in the market usually with the same business model of Amazon.

Recommendations
SWOT analysis clarifies the current standing of Amazon. Few necessary improvements are needed to be done to administer the lacking and reinforce its market position.
In short, Amazon needs to strengthen its key areas, minimize its weaknesses, avail opportunities, and counteract threats for future progress.
A few recommendations are given below:
1. Consolidate the market dominance by boosting its marketing efforts, promotional activities, and competitive advantages.
2. Strategically deal with global controversies. Amazon needs to resolve tax issues and manage its app’s features efficiently to diminish negative publicity in the market.
3. Increase its limited presence through opening physical stores outside the U.S. This will augment brand popularity and market reach.
4. Enhance its strategic entry in developing countries where many growth opportunities are available.
5. Increase competitive edges and enlarge the gap between Amazon and its biggest competitors.
6. Address the issues of counterfeit sales and cybercrimes by upgrading technology measures.
7. Enhance network security systems for the protection of consumers’ rights.
Competition
There are many competitors in the e-commerce industry, both direct and indirect. The competition in the e-commerce industry is high with a steady trend. Furthermore, the barriers to entry are low, making it easy for entrepreneurs to join and compete in the industry. Most of the competition in the industry is from domestic companies, despite this being a global industry (IBISWorld). This does pose a threat for Amazon.
(IBISWorld)
There are some key factors that IBISWorld has identified as what are strong contributions for companies in the e-commerce industry. This includes the ability to control stock on hand, ability to quickly adopt new technology, provision of superior after-sales service, and having a loyal customer base.
(IBISWorld)
While Amazon is one of the major companies in the industry, eBay is trailing behind with a large presence. Smaller companies like Overstock and Bidz manage to steal some of Amazon’s business as well.
eBay
Like Amazon, eBay opened its digital doors in 1995. The company’s vision was to sell products at a fair price that anyone in the world could purchase. eBay’s business model differs from Amazon’s as it follows an auctioning model. Here, sellers pay a small fee to the company and make arrangements for goods to be shipped to the buyer (Sinclair 15).
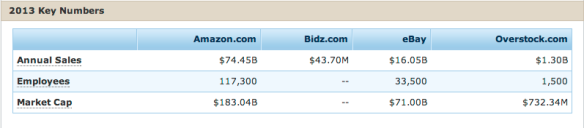
eBay only makes up 3 percent of market share, but they still manage to heavily compete (IBISWorld). This strong competition is because eBay sells merchandise worldwide and offers a variety of products just like Amazon. The company also has over 120 million users who actively use the website (Hoovers). The company also utilizes PayPal and Bill Me Later as payment assets, which many consumers favor for its easy-to-use functionality. Furthermore, eBay includes platforms like StubHub.com, Half.com, and has a stake in craigslist. The company’s net income growth in one year is 9.47 percent and they had $16.05 billion in sales for the 2013 fiscal year (Hoovers).
Overstock
Overstock came around a few years, in 1999, after the market dominators Amazon and eBay. Patrick Byrne, founder of Overstock.com, wanted to create a website for “bargain-seeking” people. The company was based on three main principles: value, investing and fair dealing (“Who we are”). Overstock business model is to liquidate the surplus of inventory on his website. This means that a large majority of the goods sold on Overstock comes from manufacturers overproduction, following Byrne’s plan.
While Amazon does not actively place television commercials, Overstock has been known to do so. These commercials have featured well-known celebrities including Jason Mraz and Ne Yo.
Amazon employs over 80,000 people, Overstock has a much smaller overhead with only 1,500 employees. In 2013, the company has a steady growth of 18.64 percent for one-year sales growth, a market value of $341.97 million, a net income of $88.51 million, and had $1.30 billion in sales (Hoovers).
Bidz.com
Bidz.com is significantly smaller than Amazon, eBay, and Overstock. The company was founded in 1998, but acquired by Glendon Group in 2012. The business model of Bidz.com is similar to dollar store discounts, an auction house, and online convenience mixed into one e-commerce store. For example, a product is put up for sale where it is then auctioned off with the starting price of $1.
Even smaller than Overstock, Bidz.com only employs 175 people and hasn’t seen employee growth in quite some time. Bidz.com has experienced some financial rollercoasters, contributing to why it was acquired by Glendon Group. Nevertheless, it is estimated that Bidz.com had an estimated $43.7 million in annual sales in 2013 (Hoovers).
Distribution
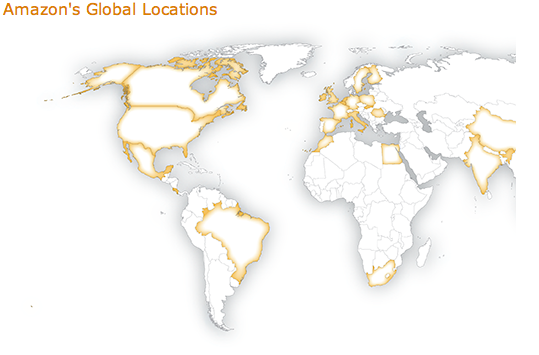
Amazon is headquartered in Seattle, Washington, but the company has offices, distribution centers, and customer service centers across the globe (“Global Locations”). Amazon strives to have all products in their fulfillment centers at all times to ensure people can purchase any item they want.
In North America alone the company controls 54 fulfillment centers. This number does not even include the subsidiary companies that Amazon owns like diapers.com. Their office located in Phoenix, Arizona is one of the largest, with the equivalent size of 28 football fields (Dickey, 2012).
Outside of North America the company manages an estimated number of 51 fulfillment centers throughout the UK, Germany, France, Italy, Czech Republic, Poland, China, Japan, and India (“Amazon Fulfillment Center Network”).
Amazon’s strategy for locations of distribution facilities is unlike many companies. While most companies choose to have locations based on population and popular geographical locations, Amazon has been known to have locations based on state tax considerations. This allows Amazon to not charge sales tax to consumers in most states (“Amazon Fulfillment Center Network”).
(“Global Locations”)
(Dickey, 2012)
(Hoovers)
Industry
Electronic commerce, more commonly referred to as e-commerce, involves the sale of products and services via electronic means. The concept was first brought into fruition in the early 1990s when the Internet opened up its usage to commercial users. It was not for another decade though until this industry started to really boom (“E-Commerce Industry”). While this is a relatively new concept, the e-commerce and online auctions industry has become an extremely popular form of purchasing behavior in a short amount of time. The Internet has become a major platform for e-tailers, retailers that primarily sell online, which for some businesses accompany their brick-and-mortar stores and threatens others.
According to Imran Khan, managing director of Goldman Sachs, e-commerce is benefiting from several positive trends, including technological advances and changes in the market. First, the continued rollout of broadband provides people around the globe with instantaneous access to the Internet and these e-commerce websites. The stores are now at an arms reach. Second, more and more people are becoming accustomed to shopping online. There is an increase of user comfort, especially from older generations, of shopping online that is aiding e-commerce growth (Davis).
There are other factors driving the supply chain for e-commerce as well. The increasing percentage of households with at least one computer paired with the continued rollout of broadband is a huge benefit. The US Census Bureau’s Current Population Survey, CPS, questions people on their computer ownership. With the cost of computers decreasing, household computer ownership steadily increased. Within a decade, the ownership of computers increased tremendously, with 56.3 percent of Americans owning a computer in 2001 and 75.6 percent in 2011 (“Current Population Survey, July 2011”). Furthermore, in 2008, 71.1 percent of Americans owned a computer compared to the estimated 78.5 percent who owned one in 2013 (IBISWorld).
The increased number of households with a computer and wider access to broadband access has increased Internet traffic overall as well. In the late 1990s, Internet traffic nearly doubled every 100 days for three successive years. This growth has been steady and continuous in the years to follow as well (Carayannis, Alexander, and Kirkwood). In the upcoming years to 2018, it is predicted that the total Internet traffic volume will increase another 21.3 percent, totaling 108.4 exabytes per month (IBISWorld).
The opportunity that is brought to both businesses and consumers is what drives the e-commerce industry. Small businesses are now able to sell specialized products that consumers are generally unable to find in stores. This allows these small businesses and entrepreneurs to stay in business for little to no overhead costs (“E-Commerce Industry”). Consumers are also able to easily compare products features, benefits, and prices with e-commerce. The ease of moving about from one store to another is not a hassle as it is just a few mouse clicks away instead of potentially miles away.
With all of these changing trends towards digital media, it is no surprise that the number of online retailers and auction sites has increased at an average annual rate of 2.5 percent to an estimated 51,073 businesses in the past five years (IBIS World). Morgan Stanley’s research team conducted research to report on global e-commerce. The study shows that e-commerce currently generates approximately 6.5 percent of all retail sales with it predicted to increase to 10 percent by 2016 (Kawa, 2013).
The story also identified companies that were best positioned to remain in the e-commerce industry. The two key players of this industry are Amazon and eBay. While not listed on Morgan Stanley’s list, Overstock and Bidz are both close competitors for Amazon as well. Furthermore, the e-commerce industry has low barriers to entry, making it easy for small businesses and entrepreneurs to compete (Gendler).
Pricing Policies
Amazon follows the “low price guarantee” model and lists their payment, pricing, and promotion information directly on their website. One way Amazon proves to be competitive is matching prices on eligible items with select retailers. This even includes retailers who sell goods on the Amazon website (“About Price Matching”).
A second pricing strategy for Amazon is it includes the list price on all products, which is the full retail price of the product (“About List Prices”). Amazon does include a surcharge for oversized or heavy items though. The company regrettably notes this on their website, but does include the fee on the detail page for the product (“About Surcharges”).
Finally, Amazon offers a refund should you purchase a product and the cost lowers within a seven day delivery date (Elliot, 2013).
Product or Service
(IBISWorld)
As one of the largest global e-tailers, Amazon sells a large variety of both products and services. The company has expanded tremendously from its initial origin of an online bookstore. Below, you will see a detailed list containing many, but not all, of the products and services that the company offers (DataMonitor360).
Books:
- Books
- Kindle Books
- Children’s Books
- Textbooks
- Audiobooks
- Magazines
Movies, music and games:
- Movies
- Blu-ray
- Amazon instant video
- MP3 downloads
- Musical instruments
- Video games
- Digital games
- Game downloads
Electronics and computers:
- TVs
- Home audio and theater
- Camera, photo and video
- Cell phones and accessories
- MP3 players and accessories
- Car electronics and global positioning system
- Electronic accessories
- Laptops, tablets and netbooks
- Desktops and servers
- Computer accessories and peripherals
- External drives, mouse, and networking
- Computer parts and components
- Software Personal computer games
- Printers and ink
- Office and school supplies
Home, garden and tools:
- Kitchen and dining
- Furniture and decor
- Bedding and bath
- Appliances
- Patio, lawn and garden equipment
- Home improvement supplies
- Power and hand tools
- Lamps and light fixtures
- Kitchen and bath fixtures
- Hardware
- Arts, crafts and sewing
- Pet supplies
Grocery, health and beauty:
- Grocery and gourmet food
- Wine
- Natural and organic food
- Health and personal care products
- Beauty products
Toys, kids and baby:
- Toys and games
- Baby products
- Clothing (kids and baby)
- Video games for kids
Clothing, shoes and jewelry:
- Clothing
- Shoes
- Handbags and accessories
- Luggage
- Jewelry
- Watches
Sports and outdoors:
- Exercise and fitness equipment
- Outdoor recreation
- Hunting and fishing
- Cycling
- Athletic and outdoor clothing
- Team sports
- Golf
- Boating and water sports
- Fan shop
- All sports and outdoors
Automotive and industrial:
- Automotive parts and accessories
- Automotive tools and equipment
- Tires and wheels
- Motorcycle and ATV Industrial and scientific
Services:
- Web services
- Order fulfillment
- Co-branded credit cards
This list shows just a glimpse of industries that Amazon takes part in selling. It is difficult to list everything, which is one of Amazon’s strengths. People love that it is essentially a one-stop-shop. In fact, some people call Amazon “Earth’s biggest everything store”, a transition the company made from the “largest bookstore.” Not all of these products and services are available worldwide though. Amazon has regional products and services. You are able to see a full list of what is offered where online at Amazon Web Services.
One of Amazon’s most well known products is its e-reader, the Kindle Fire. The Kindle, which launched in 2007, competes with the Barnes & Noble Nook and Apple iPad. The Kindle acts as both a tablet an e-reader, unlike the Nook. Furthermore, the product is sold at a much lower cost as the iPad. This positions the product perfectly in the market. Amazon currently sells more e-books than they do print books. To expand their presence online and in the e-book market even further, Amazon purchased Goodreads in 2013, a social media online book community used by over 30,000 book clubs (Hoovers). Moreover, Amazon entered the self-publishing industry allowing the company to print books on a demand basis (di Stefano, 2012).
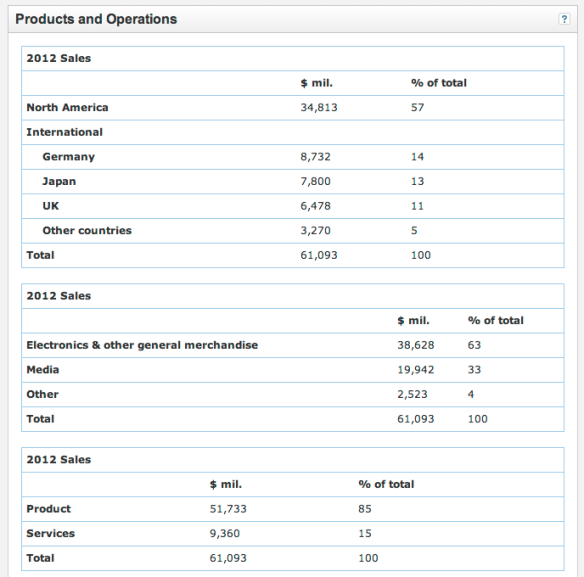
Amazon’s products consist of 85 percent of the company’s sales (Hoovers). But, along with all of these products, Amazon offers services that make up the remaining 15 percent. These services include self-publishing, online advertising, e-commerce platform, hosting, and a co-branded credit card.
Amazon Prime is another strategic service meant to boost membership. The program was launched in 2005 as a customer loyalty program. The membership starts at yearly fee of $79 that then provides customers with free two-day shipping or $3.99 one day shipping for every order. Along with that, the service allows people at access movies and TV shows through Amazon Instant Video, something that competes with Netflix. The company has later defined the Amazon Student and Amazon Mom programs that are a continuation of the original Amazon Prime (Gray, 2012).
Amazon Web Services is a great tool for web developers. The company is continuously updating this service to stay current with technological advances and trends. Amazon Web Services includes Cognito, Zocalo, SNS, and Mobile Analytics. Cognito allows developers to store and manage data. Zocalo is newer than the other services. It is a storage and sharing service that many developers can really utilize. Amazon SNS allows developers to send notifications to several devices. Finally, the Amazon Mobile Analytics allows developers to track users and collect analytical information (Snyder, 2014).
The company is constantly developing newer and better strategies to stay at the top of the e-commerce industry. This year, in 2014, Amazon is planning to break into a new industry to compete with services like Yelp, Angie’s List, Craigslist, and TaskRabbit (Di Stefano, 2014). The marketplace is one for local services including babysitters, handymen, and more. The company has been speaking with startup companies in Seattle and San Francisco that already connect service providers with customers (Seetharaman, 2014). Amazon’s strategy is to have a service paired with just about every product they sell on their website, making it difficult for competitors to even compete.
Promotion
Amazon does not engage in large campaigns or million dollar SuperBowl advertisements. The company has devised a marketing strategy that is focused on six pillars: it offers products and services, has a customer-friendly interface, scales easily from small to large, exploits its affiliate’s products and services, uses existing communication systems, and utilizes universal behaviors and mentalities. The logic is simple, because the products and services are offered online the advertising should be seen there as well. This has been something seen throughout time as the company spent $80 million in offline advertising in the fourth quarter of 1999, but only $9.4 billion in the fourth quarter of 2009 (“Marketing Strategies of Amazon.com”).
Amazon’s marketing techniques are primarily done online and with a strong pronouncement of quality to the marketplace. Pay Per Click Advertising has not been one of the company’s most beneficial methods of advertising, but the company continues to purchase such advertisements. The company regularly places advertisements on the left side of Google’s search page to diferct potential consumers to their website. Clickriver, later replaced by ProductAds, was a Pay Per Click program that allowed vendors to place ads on the company’s website. It was modeled after Google’s Pay Per Click program (“Marketing Strategies of Amazon.com”).
As Amazon was one of the first e-commerce websites, the company continuously makes subtle changes to their website. The company does not make any drastic redesigns as to not upset consumers, but continual improvement is key. Amazon is constantly seeking perfection and spending millions of dollars to recognize issues on the website and develop solutions (“Marketing Strategies of Amazon.com”).
One of Amazon’s largest marketing strategies is actually free. Permission marketing in the form of email marketing is an opportunity that Amazon fully engages in. Amazon tailors marketing emails sent to consumers based on their purchase behavior. This direct marketing really grabs the attention of potential consumers in the most cost-effective way.
Sales History
(Hoovers)
The majority of Amazon’s sales and profits come from the sales of electronics and other products. In 2013, the company reported $74.45 billion in net sales, with the majority of sales being in North America (Statista).
(Statista)
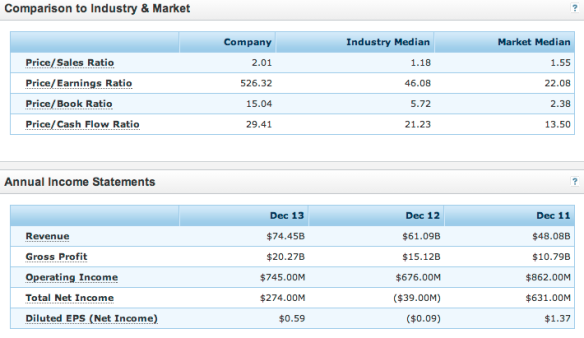
The 2014 press release by Amazon states that company had a 20 percent increase of net sales to $25.59 billion within the fourth quarter of 2013 compared to the fourth quarter of the prior fiscal year, which was $21.27 billion. Throughout the whole year, the net sales were on par with that of the fourth quarter, with a 22 percent increase to $74.45 billion (“Amazon Booms in 2013 With $74.45 Billion in Revenue”, 2014). These huge financial gains were in part due to some relatively newer products and services that have hit the market.
The press release continues to state projections for the year 2014. Amazon predicted that the net sales would be between $18.2 billion and $19.9 billion in the first quarter. This means that the growth would be between 13 percent and 24 percent (“Amazon Booms in 2013 With $74.45 Billion in Revenue”, 2014).
Sales Force
With Amazon being one of the largest e-commerce websites and an international company, it is no surprise the sales forces is equally as large. Amazon has approximately 88,400 employees (DataMonitor360). In 2012, Amazon hired an addition 50,000 people to assist with the demand of e-commerce products in the holiday season (Dickey, 2012).
Employees assist in all areas of the company from retail, seller services, e-commerce platforms, general operation, customer service, Amazon Web Services, digital, finance and administration, human resources, and legal.
Share of Market
According to Statista, almost 40 percent of Internet users worldwide have purchased products or goods online through an electronic medium such as a desktop computer, tablet, or mobile device. This percentage equates to over one billion online buyers. The digital buyer penetration is expected in increase to 45.1 percent by 2017 (Statistics & Market Data).
Every sector of e-commerce has continued to grow and the trend is projected to continue. In 2013, business-to-consumer e-commerce sales were over 1.2 trillion dollars (Statistics & Market Data).
Amazon’s computing services platform, Amazon Web Services, maintains a large share of the web services market. The service is a part of the infrastructure as a service, or IaaS, market. In 2013, Amazon Web Services equated to 37 percent of the IaaS $9 billion market. Amazon Web Services is growing at a rate of 60 percent, which is much higher than the market rate at 45 percent (D’Onfro, 2014).
In Amazon’s book market, they were also in the lead of market share. When Borders went under, the customers were divided to other companies in the market. In 2012, Amazon’s share of book spending was up to 29 percent in the first quarter, compared to Barnes & Noble’s, which was at 20 percent (Milliot, 2012).
Forrester research has shown growth in the future of the e-commerce market. While the online market only accounts for eight percent of total retail sales in the United States, Amazon’s growth shows the future growth of the market as a whole. Forrester projects that over the next five years there will be a compounded annual growth rate of nine percent (“How Amazon Plans On Driving Future Growth”, 2013). This is not just limited to the United States either. E-commerce growth is a trend across the globe. In international markets like the Asia-Pacific region, sales increased to $332 billion that is over 33 percent in 2012 (“How Amazon Plans On Driving Future Growth”, 2013).
(Hoovers)
The Market
The e-commerce market encompasses all business-to-business, business-to-consumer, and consumer-to-consumer sales. The market is relatively difficult to calculate the overall size due to the fact that very few research companies measure all of these sectors.
Amazon markets to consumers of all ages and with a variety of interests. This, in part, is due the large variety of products and services the company has to offer, as mentioned previously. According to Forrester Research, approximately 60 percent of consumers shop online at a quarterly basis. This shows just how large of the population utilizes e-commerce websites. The company’s search engine is able to segment consumers based on purchase behavior (MacLeod, 2006).
Age is one of the largest ways to segment Amazon consumers. The largest age group of online shoppers is those between the ages of 31 to 44 with the least likely being those who are 66 or older.
While consumers between the ages of 18 to 30 are the most likely to respond to online advertising and engage the most in online behaviors, this age group has a smaller discretionary income. Along with that, this age group primarily purchases items like clothing, footwear, and electronic devices online.
Those between the ages of 31 to 44, the ones accountable for the most revenue, purchase higher-priced goods and services than the younger group. These products are typically larger electronics and discretionary items. Furthermore, Forrester Research shows that 68 percent of this age group shops online on a regular basis.
Those between the ages of 45 to 54 still account for a decent amount of revenue, but they tend to care more about convenience than price.
The next age group is consumers aged between 55 and 65. This group was at one point concerned with Internet fraud or unsure of how to work the technology. Those who have moved past this mostly purchase collectibles and antiques because of the high amount of disposable income. This accounts of 20.4 percent of revenue.
Finally, those over the age of 66 generate the least revenue for e-commerce websites like Amazon. The is largely due to the unfamiliarity of technology (IBISWorld).
(IBISWorld)
Income, while it does correlate with age, is another factor. Studies have showed that consumers who are more likely to engage in online shopping have a higher income than those who won’t engage in online shopping (Black).
Social Media
Instagram LinkedIn Pinterest Snapchat TikTok Twitter YouTube
Alphabet Amazon Coca-Cola Costco Ebay Home Depot KFC McDonald’s Mountain Dew Nestle Starbucks Uber Snack Food